Rapid vs. Fast-Acting Insulin: Clinical Differences and Perioperative Use
Endocrinology
Rapid vs. Fast-Acting Insulin: Clinical Differences and Perioperative Use
Understand the key differences between rapid-acting insulin analogs and fast-acting regular insulin. Learn when to use each, including perioperative management, meal-time dosing, correctional therapy, and inpatient IV insulin use.
On this page
Rapid vs. Fast-Acting Insulin: What You Should Know
Insulin therapy is foundational in managing diabetes, but the terminology around “fast” versus “rapid” acting insulins often causes confusion. Here’s a clear breakdown for clinicians.
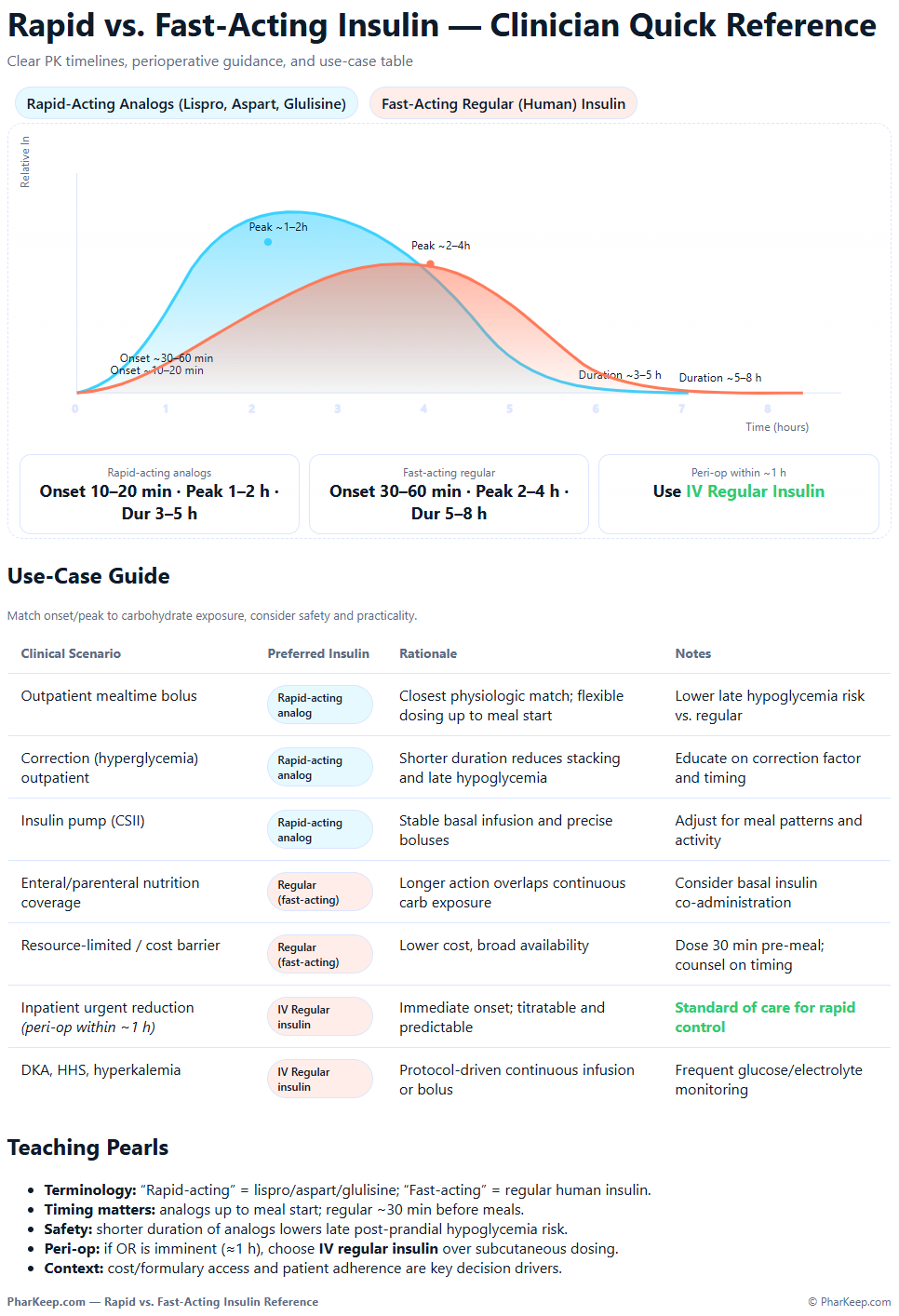
🔹 Definitions
- Rapid-acting insulin analogs: Lispro, Aspart, Glulisine.
- Fast-acting insulin: Regular human insulin.
🔹 Pharmacokinetic Differences
| Feature | Rapid-Acting Analogs (Lispro, Aspart, Glulisine) | Fast-Acting Regular Insulin |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | 10–20 min | 30–60 min |
| Peak | 1–2 hrs | 2–4 hrs |
| Duration | 3–5 hrs | 5–8 hrs |
| Timing | Up to meal start | 30 min pre-meal |
| Formulation | Modified to prevent hexamers → faster absorption | Hexameric → slower absorption |
🔹 Clinical Use Cases
Rapid-acting analogs
- Preferred for mealtime boluses (flexible dosing).
- Used in insulin pumps.
- Safer for correctional doses due to shorter action.
Fast-acting regular insulin
- IV use in hospitals (DKA, hyperkalemia, perioperative control).
- Subcutaneous bolus in resource-limited settings or where analogs are unavailable.
- Sometimes used with enteral/parenteral nutrition.
🔹 Perioperative Consideration
When surgery is within 1 hour and glucose must be lowered promptly:
- IV regular insulin is the drug of choice.
- Subcutaneous analogs or regular insulin are not appropriate due to slower and less predictable absorption.
🔹 Practical Pearls for Providers
- Match insulin onset/peak to the timing of meals.
- Use analogs for outpatient boluses and flexibility.
- Use IV regular insulin for urgent, inpatient, or perioperative needs.
- Consider cost and availability when choosing therapy.
✅ Bottom Line:
- Rapid-acting analogs → outpatient mealtime and correction.
- Fast-acting regular insulin → IV in hospital, perioperative, and when analogs are not available.
https://info.pharkeep.com/rapid-vs-fast-acting-insulin.html
Related Article
Insulin and Dextrose for Hyperkalemia: Clinical Guide, Protocols, and Safety Pearls
Learn the evidence-based use of IV regular insulin with dextrose for acute hyperkalemia management. Includes dosing, timing, when to use D50W vs D5W, and hypoglycemia prevention.


